قواعد grammar اللغة الإنجليزية ,دروس الثانية باك
محتويات المقال
- قواعد grammar اللغة الإنجليزية ,دروس الثانية باك
- Future Perfect Tense
- يستخدم زمن المستقبل التامللتعبير عن حدث متوقع حدوثه و انتهاؤه في زمن ما في المستقبل. و يأتي مع ظروف زمنية مثل By – At – By the time – before – In..Time – This time next.. Structure: will + have + past participial Examples: 1- At 6 O'clock, I will have left school 2- By June 10th, we will have taken our final exam 3- By the time I get my Visa, I will have traveled abroad 4- In five years time, I will have got married 5- I will have gone to bed before 11 O'clock 6- This time next month, we will have graduated 7- When the teacher is 65, he will have retired
- Past Perfect Tense
- يستخدم زمن الماضي التام للتعبير عن حدث حصل و انتهى في لحظة ما في زمن الماضي. و يأتي عادة مع ظروف زمنية مثل After – before – as soon as – which Structure: had + past participial Examples: 1- I had washed before I prayed 2- He went home after he had finished his work 3- He had eaten the cake which he bought 4- As soon as they had bought a car, they drove to Rabat
- Regretting Past actions
- للتعبير عن الندم على أحداث مضت و كانت نتيجتها مخيبة للأمل أو عاقبتها وخيمة, نستعمل العبارات الآتية If only – I wish – I should have – I ought to have مثال لحالة الندم: استمريت في التدخين رغم نصائح الآخرين, إلى أن أصابني داء السرطان الذي لا يرجى علاجه Examples: - If only / I wish I had given up smoking - ياليتني أقلعت عن التدخين - I should have / I ought to have taken the advice - كان من الأجدر بي أن آخذ بنصائح الآخرين
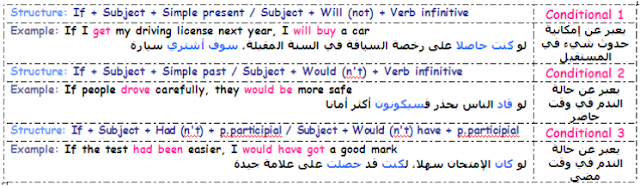
- Conditional
- الجملةالشرطية:هي الجملة التي تضم نتيجة تقتضي سببا يجب فعله لتتحقق هذه النتيجة, و هنا سندرس 3 أنواع فقط
- Active & Passive Voice
- المبني للمعلوم: هو الجملة التي يكون فاعلها معلوما المبني للمجهول: هو الجملة التي يكون فاعلها مجهولا أو قليل الأهمية Ahmed broke the window yesterday هذه الجملة مبنية للمعلوم أكتيف و ذلك لأن الفاعل فيها معلوم و هو أحمد The window was broken yesterday (by ahmed) هذه الجملة مبنية للمجهول باسيف و ذلك لأن فاعلها أحمد مجهول و حل مكان المفعول به
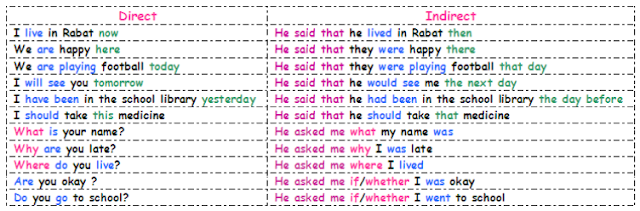
- Reported Speech
- الكلام المنقول: هو الكلام غير المباشر الذي ينوب فيه الشخص عن صاحب الكلام في نقله و الإخبار به
Future Perfect Tense
يستخدم زمن المستقبل التامللتعبير عن حدث متوقع حدوثه و انتهاؤه في زمن ما في المستقبل. و يأتي مع ظروف زمنية مثل
By – At – By the time – before – In..Time – This time next..
Structure: will + have + past participial
Examples:
1- At 6 O'clock, I will have left school
2- By June 10th, we will have taken our final exam
3- By the time I get my Visa, I will have traveled abroad
4- In five years time, I will have got married
5- I will have gone to bed before 11 O'clock
6- This time next month, we will have graduated
7- When the teacher is 65, he will have retired
يستخدم زمن المستقبل التامللتعبير عن حدث متوقع حدوثه و انتهاؤه في زمن ما في المستقبل. و يأتي مع ظروف زمنية مثل
By – At – By the time – before – In..Time – This time next..
Structure: will + have + past participial
Examples:
1- At 6 O'clock, I will have left school
2- By June 10th, we will have taken our final exam
3- By the time I get my Visa, I will have traveled abroad
4- In five years time, I will have got married
5- I will have gone to bed before 11 O'clock
6- This time next month, we will have graduated
7- When the teacher is 65, he will have retired
By – At – By the time – before – In..Time – This time next..
Structure: will + have + past participial
Examples:
1- At 6 O'clock, I will have left school
2- By June 10th, we will have taken our final exam
3- By the time I get my Visa, I will have traveled abroad
4- In five years time, I will have got married
5- I will have gone to bed before 11 O'clock
6- This time next month, we will have graduated
7- When the teacher is 65, he will have retired
Past Perfect Tense
يستخدم زمن الماضي التام للتعبير عن حدث حصل و انتهى في لحظة ما في زمن الماضي. و يأتي عادة مع ظروف زمنية مثل
After – before – as soon as – which
Structure: had + past participial
Examples:
1- I had washed before I prayed
2- He went home after he had finished his work
3- He had eaten the cake which he bought
4- As soon as they had bought a car, they drove to Rabat
يستخدم زمن الماضي التام للتعبير عن حدث حصل و انتهى في لحظة ما في زمن الماضي. و يأتي عادة مع ظروف زمنية مثل
After – before – as soon as – which
Structure: had + past participial
Examples:
1- I had washed before I prayed
2- He went home after he had finished his work
3- He had eaten the cake which he bought
4- As soon as they had bought a car, they drove to Rabat
After – before – as soon as – which
Structure: had + past participial
Examples:
1- I had washed before I prayed
2- He went home after he had finished his work
3- He had eaten the cake which he bought
4- As soon as they had bought a car, they drove to Rabat
Regretting Past actions
للتعبير عن الندم على أحداث مضت و كانت نتيجتها مخيبة للأمل أو عاقبتها وخيمة, نستعمل العبارات الآتية
If only – I wish – I should have – I ought to have
مثال لحالة الندم: استمريت في التدخين رغم نصائح الآخرين, إلى أن أصابني داء السرطان الذي لا يرجى علاجه
Examples:
- If only / I wish I had given up smoking
- ياليتني أقلعت عن التدخين
- I should have / I ought to have taken the advice
- كان من الأجدر بي أن آخذ بنصائح الآخرين
للتعبير عن الندم على أحداث مضت و كانت نتيجتها مخيبة للأمل أو عاقبتها وخيمة, نستعمل العبارات الآتية
If only – I wish – I should have – I ought to have
مثال لحالة الندم: استمريت في التدخين رغم نصائح الآخرين, إلى أن أصابني داء السرطان الذي لا يرجى علاجه
Examples:
- If only / I wish I had given up smoking
- ياليتني أقلعت عن التدخين
- I should have / I ought to have taken the advice
- كان من الأجدر بي أن آخذ بنصائح الآخرين
If only – I wish – I should have – I ought to have
مثال لحالة الندم: استمريت في التدخين رغم نصائح الآخرين, إلى أن أصابني داء السرطان الذي لا يرجى علاجه
Examples:
- If only / I wish I had given up smoking
- ياليتني أقلعت عن التدخين
- I should have / I ought to have taken the advice
- كان من الأجدر بي أن آخذ بنصائح الآخرين
Conditional
Active & Passive Voice
المبني للمعلوم: هو الجملة التي يكون فاعلها معلوما
المبني للمجهول: هو الجملة التي يكون فاعلها مجهولا أو قليل الأهمية
Ahmed broke the window yesterday
هذه الجملة مبنية للمعلوم أكتيف و ذلك لأن الفاعل فيها معلوم و هو أحمد
The window was broken yesterday (by ahmed)
هذه الجملة مبنية للمجهول باسيف و ذلك لأن فاعلها أحمد مجهول و حل مكان المفعول به
المبني للمعلوم: هو الجملة التي يكون فاعلها معلوما
المبني للمجهول: هو الجملة التي يكون فاعلها مجهولا أو قليل الأهمية
Ahmed broke the window yesterday
هذه الجملة مبنية للمعلوم أكتيف و ذلك لأن الفاعل فيها معلوم و هو أحمد
The window was broken yesterday (by ahmed)
هذه الجملة مبنية للمجهول باسيف و ذلك لأن فاعلها أحمد مجهول و حل مكان المفعول به
المبني للمجهول: هو الجملة التي يكون فاعلها مجهولا أو قليل الأهمية
Ahmed broke the window yesterday
هذه الجملة مبنية للمعلوم أكتيف و ذلك لأن الفاعل فيها معلوم و هو أحمد
The window was broken yesterday (by ahmed)
هذه الجملة مبنية للمجهول باسيف و ذلك لأن فاعلها أحمد مجهول و حل مكان المفعول به